DISCLAIMER
The information and materials accessed through or made available for use on any of our Sites, including, any information about diseases, conditions, treatments, or medicines, are for informational purposes only. The Content is not intended to be and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment, and your participation on our Sites does not create a healthcare professional-patient relationship. You should consult a doctor or other qualified health care professional regarding any questions you have about your health or before making any decisions related to your health or wellness. Call your doctor or 911 immediately if you think you may have a medical emergency.compose your message
message sent
email sent successfully
Trusted Resources: News & Events
Latest announcements and gatherings
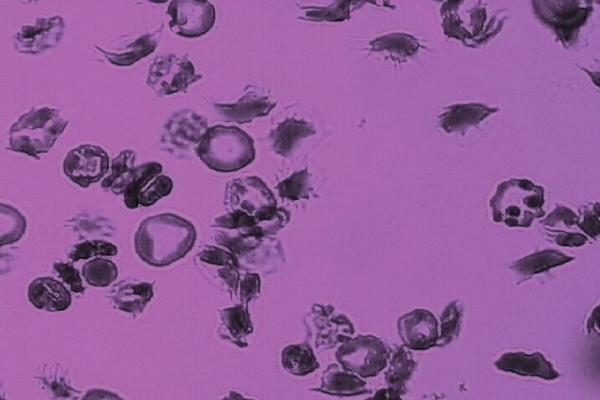
How sickled red blood cells stick to blood vessels
One of the most common complications of sickle-cell disease occurs when deformed red blood cells clump together, blocking tiny blood vessels and causing severe pain and swelling in the affected body parts.
A new study from MIT sheds light on how these events, known as vaso-occlusive pain crises, arise. The findings also represent a step toward being able to predict when such a crisis might occur.
“These painful crises are very much unpredictable. In a sense, we understand why they happen, but we don’t have a good way to predict them yet,” says Ming Dao, a principal research scientist in MIT’s Department of Materials Science and Engineering and one of the senior authors of the study.
The researchers found that these painful events are most likely to be produced by immature red blood cells, called reticulocytes, which are more prone to stick to blood vessel walls.
 +myBinder
+myBinderRelated Content
-
education & researchOutcome of severe vaso occlusive crisis in sickle cell disease adults admitted to referral centers in Africa and Eur...Introduction: Vaso-Occlusive Crisis (VOC...
-
education & researchHospitalization for Acute Pain in Sickle Cell Disease: Changes in Clinical Parameters and Factors Predicting Hospita...Introduction: Acute vaso-occlusive crisi...
-
Community CenterLiving With Sickle Cell Disease Is a Constant Battle With Pain, According to one Woman Who Has It“You don’t look sick.” That’s ...
-
news & eventsPhase 1 trial to test under-the-skin injection of sevuparin in sickle cell patientsModus Therapeutics is going to launch ...
-
news & eventsA multiple drug approach to preventing sickle cell crisisSickle cell disease is characterized by ...
-
videos & visualsSickle Cell Disease: Treatments – PAINWeekhttps://www.youtube.com/watch?v=llqCdRNK...
-
videos & visualsPatient Perspective: The Journey of Pain in Sickle Cell Diseasehttps://www.youtube.com/watch?v=F4raFO0e...
send a message
To improve your experience on this site, we use cookies. This includes cookies essential for the basic functioning of our website, cookies for analytics purposes, and cookies enabling us to personalize site content. By clicking on 'Accept' or any content on this site, you agree that cookies can be placed. You may adjust your browser's cookie settings to suit your preferences. More Information
The cookie settings on this website are set to "allow cookies" to give you the best browsing experience possible. If you continue to use this website without changing your cookie settings or you click "Accept" below then you are consenting to this.
Support for this site is provided by

This platform is made possible through a partnership with the Sickle Cell Disease Association of America, Inc. (SCDAA) and its member organizations. SCDAA's mission is to advocate for people affected by sickle cell conditions and empower community-based organizations to maximize quality of life and raise public consciousness while advancing the search for a universal cure.




